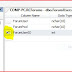
Get the HOST NAME / COMPUTER NAME
Get the Computer Name using SQL Query
Select Host_Name() as Computer_Name
Get Computer Name, Get HOst Name
Here is the Way you can get the same in Visual Basic : http://vbadud.blogspot.com/2007/05/get-computer-name.html
Here is the Way you can get the same in .Net :
http://dotnetdud.blogspot.com/2007/06/get-computer-name-in-net.html
Saturday, April 28, 2007
Coalesce Function
Coalesce Function
Displays the first nonnull expression among its arguments
-- returns Iam Not a Null
Select Coalesce (Null, Null, 'Iam Not a Null', Null) as NotNull
This function will be used to skip the NULL columns and get the ones that have value. This function can be maximum utilised in situations where you need to get one value from a group of columns that could contain null.
For example, Let us assume that you have a contact table with office_phno, mobile_nos, home_phnos in it and you need to send them greetings. You can use Coalesce Function to get the non null number according to priority
Select Coalesce (Office_phno, mobile_nos, home_phnos, 'No Ph No Available) as ContactNo

Displays the first nonnull expression among its arguments
-- returns Iam Not a Null
Select Coalesce (Null, Null, 'Iam Not a Null', Null) as NotNull
This function will be used to skip the NULL columns and get the ones that have value. This function can be maximum utilised in situations where you need to get one value from a group of columns that could contain null.
For example, Let us assume that you have a contact table with office_phno, mobile_nos, home_phnos in it and you need to send them greetings. You can use Coalesce Function to get the non null number according to priority
Select Coalesce (Office_phno, mobile_nos, home_phnos, 'No Ph No Available) as ContactNo
Labels:
Coalesce Function,
Select Statement,
SQL Server,
Sybase
CASE Function Example - Database
SQL Server CASE Function
Evaluates a list of conditions and returns one of multiple possible result expressions
Begin
Declare @Position Int;
Set @Position = 3
Select Case @Position
when 1 then 'Gold'
when 2 then 'Silver'
when 3 then 'Bronze'
Else cast(@Position as varchar)+ 'th'
End as Medal
End
You can change the value of @Position and analyse the output
SQL Server CASE Function, CASE Function, CASE Function Example
Evaluates a list of conditions and returns one of multiple possible result expressions
Begin
Declare @Position Int;
Set @Position = 3
Select Case @Position
when 1 then 'Gold'
when 2 then 'Silver'
when 3 then 'Bronze'
Else cast(@Position as varchar)+ 'th'
End as Medal
End
You can change the value of @Position and analyse the output
SQL Server CASE Function, CASE Function, CASE Function Example
Know the version of the DB
Database Version - SQL Server/ Sybase
Select @@Version
Print @@Version
Apart from the SQL Server Version, It also provides processor architecture, build date, and operating system for the current installation
The above information can also be retrieved from the following stored procedure
Exec xp_msver
Keywords: Version, xp_msver, System Stored Procedure
Select @@Version
Print @@Version
Apart from the SQL Server Version, It also provides processor architecture, build date, and operating system for the current installation
The above information can also be retrieved from the following stored procedure
Exec xp_msver
Keywords: Version, xp_msver, System Stored Procedure
Labels:
Database Version,
SQL Server,
Sybase,
System Stored Procedures,
Version,
Version of DB,
xp_msver
Selecting Database users
Selecting Database users
The following queries will be returning the user names
Select User
-- This displays the current user
Select User_Name()
Select Current_User
-- This displays the user belongint to ID 2
Select User_Name(2)
-- Displays all users for that DB
Select uid, name from sysusers order by uid
sysusers contain the information of all users
The following queries will be returning the user names
Select User
-- This displays the current user
Select User_Name()
Select Current_User
-- This displays the user belongint to ID 2
Select User_Name(2)
-- Displays all users for that DB
Select uid, name from sysusers order by uid
sysusers contain the information of all users
Friday, April 27, 2007
Check database permission
Check Access to database
Check if user has access to the specified database
HAS_DBACCESS returns 1 if the user has access to the database, 0 if the user has no access to the database, and NULL if the database name is not valid
Begin
Declare @RetValue Int;
Set @RetValue = HAS_DBACCESS('AdventureWorks')
IF @RetValue = 1
Print 'User has Access';
Else
IF @RetValue = 0
Print 'User Does not have Access';
Else
Print 'Database name is not valid';
End
Check for Valid Database Name, DB Name Error, DB Name Validity, User Permissions for DB, User Access for DB, User Rights for DB, SQL Server Check Access to database
Check if user has access to the specified database
HAS_DBACCESS returns 1 if the user has access to the database, 0 if the user has no access to the database, and NULL if the database name is not valid
Begin
Declare @RetValue Int;
Set @RetValue = HAS_DBACCESS('AdventureWorks')
IF @RetValue = 1
Print 'User has Access';
Else
IF @RetValue = 0
Print 'User Does not have Access';
Else
Print 'Database name is not valid';
End
Check for Valid Database Name, DB Name Error, DB Name Validity, User Permissions for DB, User Access for DB, User Rights for DB, SQL Server Check Access to database
NUMBER OF ACTIVE TRANSACTIONS
NUMBER OF ACTIVE TRANSACTIONS
@@TRANCOUNT shows # of active transactions for the current connection
Select @@TRANCOUNT
If you use savepoint_name in ROLLBACK TRANSACTION @@TRANCOUNT will not be affected
Begin
Begin Transaction
Save TRAN Point1 ;
Select 'The Transaction Count is ' + cast(@@TRANCOUNT as varchar) ;
-- This roll Back will not have any impact on @@TRANCOUNT
RollBack Transaction Point1
Select 'The Transaction Count is ' + cast(@@TRANCOUNT as varchar) ;
-- This roll Back will Reset the @@TRANCOUNT
RollBack Transaction
Select 'The Transaction Count is ' + cast(@@TRANCOUNT as varchar) ;
End
Keywords: @@TRANCOUNT, savepoint_name, Number Of Active Transactions
@@TRANCOUNT shows # of active transactions for the current connection
Select @@TRANCOUNT
If you use savepoint_name in ROLLBACK TRANSACTION @@TRANCOUNT will not be affected
Begin
Begin Transaction
Save TRAN Point1 ;
Select 'The Transaction Count is ' + cast(@@TRANCOUNT as varchar) ;
-- This roll Back will not have any impact on @@TRANCOUNT
RollBack Transaction Point1
Select 'The Transaction Count is ' + cast(@@TRANCOUNT as varchar) ;
-- This roll Back will Reset the @@TRANCOUNT
RollBack Transaction
Select 'The Transaction Count is ' + cast(@@TRANCOUNT as varchar) ;
End
Keywords: @@TRANCOUNT, savepoint_name, Number Of Active Transactions
Maximum Level of Nesting in SQL Server Stored Procedure
Maximum Level of Nesting in SQL Server Stored Procedure
A Maximum of 32 levels of Nesting is allowed in SQL Server Stored Procedure. When the maximum of 32 is exceeded, the transaction is terminated.
Select @@NestLevel
Returns the nesting level of the current stored procedure execution (initially 0) on the local server
Keywords: @@NestLevel, Maximum Level of Nesting
A Maximum of 32 levels of Nesting is allowed in SQL Server Stored Procedure. When the maximum of 32 is exceeded, the transaction is terminated.
Select @@NestLevel
Returns the nesting level of the current stored procedure execution (initially 0) on the local server
Keywords: @@NestLevel, Maximum Level of Nesting
Tuesday, April 24, 2007
DatePart - Get Part of the Date
-- Selecting the Current Year/Get Current Year/Separate Year Part from Date
Select DatePart(YY, GetDate()) as Current_Year
-- Selecting the Current Quarter/Get Current Quarter/Separate Quarter Part from Date
Select DatePart(QQ, GetDate()) as Current_Quarter
-- Selecting the Current Month/Get Current Month/Separate Month Part from Date
Select DatePart(MM, GetDate()) as Current_Month
-- Selecting the Name of Current Month/Get Name of Current Month/Separate Month Part from Date and display its Name
Select DateName(month, GetDate()) as Current_Month_Name
-- Selecting the Name of Current Month/Get Name of Current Month/Separate Month Part from Date and display its Name
Select DateName(day, GetDate()) as Current_Day
-- Selecting the Name of Current Month/Get Name of Current Month/Separate Month Part from Date and display its Name
Select DateName(wk, GetDate()) as Current_Week
Select DatePart(YY, GetDate()) as Current_Year
-- Selecting the Current Quarter/Get Current Quarter/Separate Quarter Part from Date
Select DatePart(QQ, GetDate()) as Current_Quarter
-- Selecting the Current Month/Get Current Month/Separate Month Part from Date
Select DatePart(MM, GetDate()) as Current_Month
-- Selecting the Name of Current Month/Get Name of Current Month/Separate Month Part from Date and display its Name
Select DateName(month, GetDate()) as Current_Month_Name
-- Selecting the Name of Current Month/Get Name of Current Month/Separate Month Part from Date and display its Name
Select DateName(day, GetDate()) as Current_Day
-- Selecting the Name of Current Month/Get Name of Current Month/Separate Month Part from Date and display its Name
Select DateName(wk, GetDate()) as Current_Week
First day of the week - @@datefirst
The first day of the week will be 7 - Sunday (default for US English)
Select @@datefirst as FirstDay
You can set it by :
Set datefirst 1;
Select @@datefirst as FirstDay
You can set it by :
Set datefirst 1;
Current Database - SQL Server
What is the Current Database?
Select DB_NAME() as Curr_DB
Select DB_NAME() as Curr_DB
Monitoring SQL SErver with SP_WHO
MONITORING SQL SERVER WITH SP_WHO
Exec sp_who
will provide information about current users, sessions, and processes in an instance of the Microsoft SQL Server Database Engine
Use the login to filter results for a particular user
Exec sp_who 'Login21'
Exec sp_who
will provide information about current users, sessions, and processes in an instance of the Microsoft SQL Server Database Engine
Use the login to filter results for a particular user
Exec sp_who 'Login21'
Maximum Connections for SQL Server
All About Connections
@@MAX_Connections Returns the maximum number of simultaneous user connections allowed on an instance of SQL Server. The number returned is not necessarily the number currently configured
Select @@MAX_Connections as Max_Connections
No of attempted connections for SQL Server
Select @@Connections as TotalLoginAttempts
This will include either successful or unsuccessful since SQL Server was last started.
You can also check the same using sp_monitor System procedure
Exec sp_monitor
@@MAX_Connections Returns the maximum number of simultaneous user connections allowed on an instance of SQL Server. The number returned is not necessarily the number currently configured
Select @@MAX_Connections as Max_Connections
No of attempted connections for SQL Server
Select @@Connections as TotalLoginAttempts
This will include either successful or unsuccessful since SQL Server was last started.
You can also check the same using sp_monitor System procedure
Exec sp_monitor
Monday, April 16, 2007
Formatting Date Input - DateFOrmat
Formatting Date Input - Jan-7 or July 1 / British Way of Date Representation / British Date
DECLARE @datevar DATETIME;
SET @datevar = '01/07/2006';
SELECT @datevar AS DateVar;
SELECT datename(month, @datevar) AS month_name;
The above will return January
SET @datevar = '07/01/2006';
SELECT @datevar AS DateVar;
SELECT datename(month, @datevar) AS month_name;
The above will return July
If you are using British way of representing dates, then '01/07/2006' is 1-July. Use dateformat to change the input to dmy system
Set DateFOrmat dmy;
GO
DECLARE @datevar DATETIME;
SET @datevar = '01/07/2006';
SELECT @datevar AS DateVar;
SELECT datename(month, @datevar) AS month_name;
The above will return July
DECLARE @datevar DATETIME;
SET @datevar = '07/01/2006';
SELECT @datevar AS DateVar;
SELECT datename(month, @datevar) AS month_name;
The above will return Jan
DateFOrmat does not affect the display of date values
DECLARE @datevar DATETIME;
SET @datevar = '01/07/2006';
SELECT @datevar AS DateVar;
SELECT datename(month, @datevar) AS month_name;
The above will return January
SET @datevar = '07/01/2006';
SELECT @datevar AS DateVar;
SELECT datename(month, @datevar) AS month_name;
The above will return July
If you are using British way of representing dates, then '01/07/2006' is 1-July. Use dateformat to change the input to dmy system
Set DateFOrmat dmy;
GO
DECLARE @datevar DATETIME;
SET @datevar = '01/07/2006';
SELECT @datevar AS DateVar;
SELECT datename(month, @datevar) AS month_name;
The above will return July
DECLARE @datevar DATETIME;
SET @datevar = '07/01/2006';
SELECT @datevar AS DateVar;
SELECT datename(month, @datevar) AS month_name;
The above will return Jan
DateFOrmat does not affect the display of date values
Universal Time or Greenwich Meridian Time (GMT)
Getting the Universal Time - GMT
Select GetDate() as LocalTime
Select GetUTCDate() as GMT_Time
GetUTCDate Returns the datetime value representing the current UTC time (Coordinated Universal Time or Greenwich Mean Time)
Select DateDiff(second,GetDate(),GetUTCDate() ) as DifferenceinSec
will give you the difference between GMT and your Local Time
Select GetDate() as LocalTime
Select GetUTCDate() as GMT_Time
GetUTCDate Returns the datetime value representing the current UTC time (Coordinated Universal Time or Greenwich Mean Time)
Select DateDiff(second,GetDate(),GetUTCDate() ) as DifferenceinSec
will give you the difference between GMT and your Local Time
Labels:
DateDiff,
Difference between GMT and Local,
GetDate,
GetUTCDate,
GMT
SQL Adding or Subtracting Dates
********************Adding or Subtracting Dates********************
If the requirement is to calculate the age of a person six months from now, dateadd function can help
Select BirthDate, DateDiff(year, BirthDate, Dateadd(month, 6, getdate())) as BirthDateAfterSix from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Desc
subtracting dates is equally easy:
Select BirthDate, DateDiff(year, BirthDate, Dateadd(month, -6, getdate())) as BirthDateAfterSix from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Desc
If the requirement is to calculate the age of a person six months from now, dateadd function can help
Select BirthDate, DateDiff(year, BirthDate, Dateadd(month, 6, getdate())) as BirthDateAfterSix from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Desc
subtracting dates is equally easy:
Select BirthDate, DateDiff(year, BirthDate, Dateadd(month, -6, getdate())) as BirthDateAfterSix from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Desc
Labels:
Adding Dates,
Dateadd,
SQL Server 2005,
Subtracting Dates,
Sybase
GetAge - Get Age Using SQL Query
How to calculate Age using SQL Query
DateDiff function can be used to get the Age from the birth date
Select BirthDate, DateDiff(year, BirthDate, getdate()) as Age from HumanResources.Employee
DateDiff function can be used to get the Age from the birth date
Select BirthDate, DateDiff(year, BirthDate, getdate()) as Age from HumanResources.Employee
Sunday, April 15, 2007
ANSI_NULLS - Equalling NULLs
********************Check For NULL********************
If you check for Null using <> or = operator, it might not return the results even if the table contains NULLs
Select * from Person.Address where AddressLine2 = Null
will not yield any results
on the otherhand it is a good practice to get the intended value using the following
Select * from Person.Address where AddressLine2 Is Null
If you still want to use = or <> with Nulls then the following will work
SET ANSI_NULLS OFF
Select * from Person.Address where AddressLine2 = Null
However, this feature will be removed in a future version of Microsoft SQL Server. Avoid using this feature in new development work, and plan to modify applications that currently use this feature.
If you check for Null using <> or = operator, it might not return the results even if the table contains NULLs
Select * from Person.Address where AddressLine2 = Null
will not yield any results
on the otherhand it is a good practice to get the intended value using the following
Select * from Person.Address where AddressLine2 Is Null
If you still want to use = or <> with Nulls then the following will work
SET ANSI_NULLS OFF
Select * from Person.Address where AddressLine2 = Null
However, this feature will be removed in a future version of Microsoft SQL Server. Avoid using this feature in new development work, and plan to modify applications that currently use this feature.
Tie in Max or Min Function - WITH TIES
If you have two employees with the same birth date - the youngest/oldest employee has a tie. Then use of WITH TIES clause will solve it.
If WITH TIES is also specified, all rows that contain the last value returned by the ORDER BY clause are returned, even if doing this exceeds the number specified by expression.
Top 1 could return two or even more rows in case of a Tie
Select TOP 1 WITH TIES BirthDate from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Desc
WITH TIES can be used to get the matching records of the last/first even if it is more than the given number or percent
WITH TIES requires an ORDER BY clause.
If WITH TIES is also specified, all rows that contain the last value returned by the ORDER BY clause are returned, even if doing this exceeds the number specified by expression.
Top 1 could return two or even more rows in case of a Tie
Select TOP 1 WITH TIES BirthDate from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Desc
WITH TIES can be used to get the matching records of the last/first even if it is more than the given number or percent
WITH TIES requires an ORDER BY clause.
Labels:
Select Statement,
SQL Server 2005,
Sybase,
UsingTOP,
WITH TIES
Youngest Employee - SQL TOP
********************Youngest & Oldest Employee********************
To get the youngest / olderst employee, two different methods are shown here.
1. Using Max and Min Functions
2. Using Top in Select Statement
'' Youngest Employee (Reference : AdventureWorks)
Select Min(BirthDate) from HumanResources.Employee
Select TOP 1 BirthDate from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Asc
Select TOP 1 * from HumanResources.Employee Order By BirthDate Asc
Select * from Person.Contact where ContactID = (Select TOP 1 EmployeeID from HumanResources.Employee Order By BirthDate Asc)
'' Oldest Employee (Reference : AdventureWorks)
Select Max(BirthDate) from HumanResources.Employee
Select TOP 1 BirthDate from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Desc

Free Search Engine Submission

AddMe - Search Engine Optimization
Homerweb Search
To get the youngest / olderst employee, two different methods are shown here.
1. Using Max and Min Functions
2. Using Top in Select Statement
'' Youngest Employee (Reference : AdventureWorks)
Select Min(BirthDate) from HumanResources.Employee
Select TOP 1 BirthDate from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Asc
Select TOP 1 * from HumanResources.Employee Order By BirthDate Asc
Select * from Person.Contact where ContactID = (Select TOP 1 EmployeeID from HumanResources.Employee Order By BirthDate Asc)
'' Oldest Employee (Reference : AdventureWorks)
Select Max(BirthDate) from HumanResources.Employee
Select TOP 1 BirthDate from HumanResources.Employee Order By 1 Desc
Free Search Engine Submission
AddMe - Search Engine Optimization
Homerweb Search
Labels:
Select Statement,
SQL Server 2005,
Sybase,
UsingTOP
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)